Nawyki żywieniowe
Lwia część rekinów to mięsożercy, choć sposób zdobywania pożywienia jest różnorodny.
Rekin wielorybi – największy rekin i zarazem największa ryba świata, to typowy filtrator zasysający plankton i małe ryby. Posiada on coś na kształt fiszbinów (swoistego sita) występujących u wielu wielorybów. Rekin wielkogębowy zachowuje się podobnie, choć może on dodatkowo przyciągać swe ofiary luminescencją tkanki wewnątrz pyska.
Rekin foremkowy (Isistius brasiliensis) ma ogromne zęby w stosunku do swej wielkości, a dolny zestaw jest wyjątkowo ostry. Wydaje się, że w czasie polowania chwyta swoją ofiarę, przytrzymuje, a następnie wsysa się w ciało dzięki grubym wargom i odrywa płat mięsa.
Gatunki zamieszkujące dno morskie mogą polować poprzez zasadzkę dzięki umiejętnościom kamuflażu. Dotyczy to głównie rekinów dywanowych z rodziny brodatkowatych (Orectolobidae) oraz raszplokształtnych z rodzaju Squatina. Wiele gatunków dennych poluje niemal wyłącznie na skorupiaki, które miażdżą swoimi zębami. Duże gatunki takie jak żarłacz biały zjadają małą zdobycz w całości, natomiast z dużej zdobyczy odgryzają ogromne płaty mięsa. Niektóre rekiny lubią polować stadnie, np. rekin rafowy białopłetwy (Triaenodon obesus).

Tryb życia
Rekiny kojarzą nam się najczęściej z samotnymi myśliwymi. Prawda tego stwierdzenia jest tylko połowiczna. Zaledwie bowiem parę gatunków prowadzi samotniczy żywot. Większość rekinów jest dobrze uspołeczniona.
Wiele z nich pokonuje również wiele tysięcy kilometrów w poszukiwaniu pożywienia i miejsc do rozrodu. Naukowcy sądzą, że wzorce migracji rekinów są bardziej skomplikowane, niż te u ptaków.
Jednymi z najbardziej społecznych rekinów są niektóre młotowate. Mogą one tworzyć stada złożone z ok. 100 osobników gromadzących się wokół gór podwodnych oraz wysp.
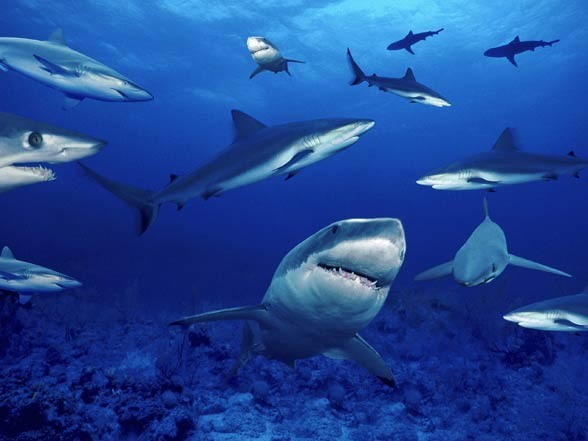

Wyporność
W przeciwieństwie do ryb kostnoszkieletowych rekiny nie posiadają pęcherza pławnego wypełnionego gazem umożliwiającym pływalność. Te drapieżne ryby muszą radzić sobie inaczej. Do utrzymywania się w toni wodnej wykorzystują bardzo dużą wątrobę, wypełnioną oleistą substancją zawierającą skwalen. W pływaniu z pewnością pomaga również chrzęstny, lekki szkielet.
Większość rekinów musi pływać cały czas aby móc oddychać i nie opaść na dno. Istnieją jednak gatunki zdolne do pompowania wody przez skrzela w bezruchu, one jako wyjątek mogą odpoczywać na dnie zbiornika wodnego. Do szczęściarzy tych zalicza się rekin wąsaty (Ginglymostoma cirratum).
Rozmnażanie
Rekiny realizują tzw. strategię K. Oznacza to, że wydają one na świat jednorazowo małą liczbę młodych, które mają większą szansę na przetrwanie do okresu dorosłości. Ryby te dojrzewają jednak powoli w stosunku do innych ryb, np. żarłacz żółty (Negaprion brevirostris) osiąga dojrzałość płciową dopiero w 13-15 roku życia.

Rodzaje zapłodnienia
Płciowe
Dochodzi do niego wewnątrz ciała samicy. Samiec używa do tego narządu kopulacyjnego ulokowanego na spodniej części ciała. Jest to odpowiednik penisa u ssaków. Kopulacja z reguły nie jest poprzedzona zalotami.
Samice dużych gatunków mają po kopulacji często ślady ugryzień, będące „pamiątką” po samcu, który trzymał zębami partnerkę w czasie aktu płciowego.
Podejrzewa się, że podobne ślady mogą pozostawać po zalotach – samce okazują zainteresowanie daną samicą poprzez gryzienie. Co ciekawe, u samic niektórych gatunków rekinów pojawia się grubsza skóra, chroniąca lepiej przed urazami tego typu.

Bezpłciowe
Wśród rekinów udokumentowano 2 razy przypadek, w którym samice nie wchodząc w relację seksualną z samcem poczęły młode. Okazuje się więc, że wśród tych ryb może pojawiać się zjawisko partenogenezy, czyli dzieworództwa. Naukowcy uważają, ze tego typu zapłodnienie to „ostatnia deska ratunku” w sytuacji, gdy w pobliżu nie ma partnera chętnego do kopulacji.
Rozmnażanie bezpłciowe skutkuje jednak zmniejszeniem różnorodności genetycznej, która jest niezbędna w tworzeniu ochrony przed zagrożeniami. Wydaje się, że rozmnażanie bezpłciowe mogło przyczynić się do spadku irlandzkiej populacji żarłacza błękitnego (Prionace glauca).

W obrębie grupy rekinów spotyka się 3 rodzaje rozmnażania:
Żyworodność lecytotroficzną
Żyworodność lecytotroficzna (zwaną dawniej jajożyworodnością) – występuje u większość rekinów. Po zapłodnieniu w ciele matki rozwijają się jaja wyposażone w żółtko i płyny odżywiające płód. Gdy nadchodzi moment porodu, młode jest w pełni rozwinięte. U lamnokształtnych dochodzi do tzw. oofagii – zarodki, które jako pierwsze wykluły się w ciele samicy, zjadają niewyklute jaja. U tawrosza piaskowego (Carcharias taurus) młode zjadają swoje rodzeństwo.
Jajorodność
Jaja są składane w wodzie. Młode są chronione skórzastą osłonką. Puste jaja często można obserwować na plażach, mają one bardzo charakterystyczny kształt (czasem nazywane są mermaid’s purse). Do gatunków jajorodnych zaliczamy m.in. rekinkowate (Scyliorhinidae), rogatkokształtne z gatunku Heterodontus francisci i Heterodontus portusjacksoni.
Żyworodność
Pewna liczba gatunków rekinów tworzy łożysko w czasie ciąży. Młode rodzą się w pełni rozwinięte. Do rekinów żyworodnych zaliczają się głównie żarłaczowate, w tym wspomniany już żarłacz błękitny oraz przedstawiciele rodzaju Mustelus.
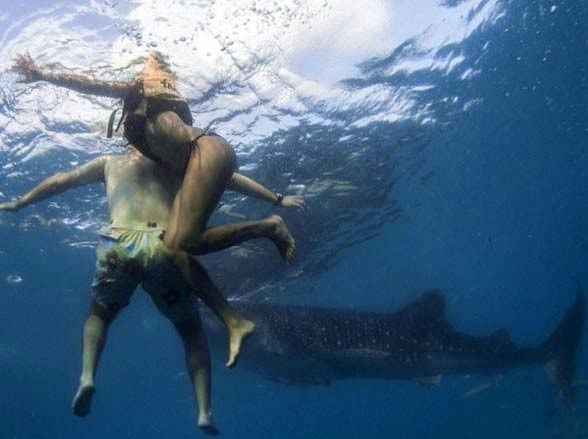

Ataki rekinów na ludzi
W 2006 The International Shark Attack File – światowa baza danych zbierająca informacje o atakach rekinów na ludzi, sprawdziła 96 domniemanych ataków. Spośród nich 62 były atakami niesprowokowanymi, a 16 wywołane zostały ludzką natrętnością. Średnia liczba ofiar śmiertelnych w latach 2001-2006 na skutek niesprowokowanego ataku wynosi 4,3.
Powyższe wyniki pokazują, że na świecie żyje tylko kilka groźnych dla ludzi gatunków rekinów. Spośród ok. 500 gatunków tylko 4 były wymienione w znacznej części śmiertelnych ataków nie wynikających ze sprowokowania.
Rekiny stanowiące zagrożenie dla ludzi
Rekiny, których należy się obawiać:
- żarłacz biały
- żarłacz białopłetwy (Carcharhinus longimanus),
- żarłacz tępogłowy
- żarłacz tygrysi.
Jednocześnie są to jedne z największych rekinów i ze względu na swe potrzeby polowania na dużą zdobycz, mogą atakować i zabijać ludzi. Kwestia tego czy im smakujemy została wyjaśniona w artykule o żarłaczu białym, zwanym też ludojadem.
Jednym ze sposobów uniknięcia ataku ze strony rekina jest zdejmowanie przed kąpielą w morzu / oceanie biżuterii i elementów metalowych, które w wodzie mocno błyszczą. Nie należy również zbyt intensywnie chlapać się w wodzie, ponieważ to pobudza duże rekiny do ataków.

Najdłużej żyjący rekin
Najdłużej żyjącym rekinem i jednocześnie najdłużej żyjącym kręgowcem jest rekin polarny (Somniosus microcephalus). Rekiny te zdolność do rozmnażanie uzyskują w przedziale 134 – 178 lat… Maksymalna oszacowana długość ich życia wynosi 392 lata ± 120 lat, co daje minimum na poziomie 272 a maksimum na poziomie 512 lat… Badanie to wykonane zostało na samicy o długości 502 cm. Wyniki badań opublikowane zostały w sierpniu 2016 roku.
Szczegółowe dane/wymiary
Rekiny
- Długość ciała: 0,17 – 12,65 m (niepotwierdzone do 20 m) – najmniejszym znanym rekinem jest słabo poznany przedstawiciel koleniokształtnych z gatunku Etmopterus perryi. Największym rekinem świata jest rekin wielorybi (Rhincodon typus).
- Waga: do 13,6 t (niepotwierdzone do 20 ton)
- Długość życia: 20-100 lat i dłużej, wiek rekina uzależniony jest od gatunku. Najdłużej żyjące rekiny, to rekiny polarne, ich maksymalną długość życia oszacowano na 272-512 lat (błąd wynikający z niedokładności szacowania metodą datowania radiowęglowego).

Rekiny – ciekawostki
- Nazwa rekin pochodzi z języka francuskiego – requin.
- Czy rekiny występują w Bałtyku? Odpowiedź na to pytanie zamieściliśmy w artykule: Rekiny – zabójcy z głębin.
- Najstarsze skamieniałości rekinów datuje się na ordowik, czyli 450-420 mln lat temu. Istniały one zatem jeszcze przed powstaniem kręgowców lądowych oraz przed kolonizacją roślin.
- Rekiny spotkano w gorącej wodzie otaczającej podwodny aktywny wulkan Kavachi, ulokowany w południowo–zachodnim Pacyfiku.
- Rekin może tracić nawet 30 000 zębów w ciągu swego życia. Liczba ta zależna jest od danego gatunku.
- Rekiny widzą w ciemnościach 10-krotnie lepiej niż człowiek.
- Większość rekinów jest zmiennocieplna. Oznacza to, że temperatura ich ciała jest taka sama jak otaczające je środowisko.
- Niektóre rekiny mogą zapadać w tzw. pozorną śmierć. Jest to metoda ochrony przed wrogiem. Rekin obracany lub dotknięty w nos zastyga niczym martwy.
- Współczynnik masy ciała do masy mózgu u rekinów jest podobny do tego u ssaków i ptaków. Oznacza to, ze są one inteligentne, co przejawia się na wolności zachowaniami wskazującymi na zabawę.
- Wątroba może stanowić ok. 30% masy ciała rekina.
- Rekiny są obecne w mitologii hawajskiej.
- Do wieku XVI marynarze nazywali rekiny morskimi psami / wilkami.



















Zszokowała mnie długość życia rekina polarnego :O
rekiny mają większe prawo pływać w oceanach niż pier….ony homo sapiens śmierć kłósowniką żeby im kończyny poobcinać i wrzucić do wody
Dokładnie tak. Niestety człowiek mordujący zwierzęta nie jest nazywany mordercą, ale myśliwym. Nie jest też nazywany zwyrodnialcem, czy psychopatą, choć gdy morduje czy okalecza zwierzęta /np. rekiny/ robi to, bo sprawia mu to przyjemność.
Właśnie.
Po pierwsze naucz się pisać a po drugie jeżeli uważasz przy okazji samego siebie za pier… homo sapiens bo też tym gatunkiem stworzenia jesteś to idź się zastrzel, nie rozumiem jak można być takim kretynem, i szczerze gdybym miał czas i możliwości sam bym się pobawił w polowanie i uważam że każdy człowiek jest ważniejszy od zwierzęcia czy to pies kot czy rekin, i wasze idiotyczne argumenty bo zwierzęta czują na mnie nie działają z prostej przyczyny muszą czuć to jest oczywisty mechanizm biologiczny który także występuje u nas ludzi. Wiele z was osób co tak pisze jak ty nawet nie zdaje sobie sprawy jak działa natura macie chore wyobrażenia na temat zwierząt i ich idealizowanie poczytaj o zjawisku zwanym syndromem bambiego.
Może weganie?
„I szczerze gdybym miał czas to sam chętnie pobawilbym bym się w strzelanie” o ile by Cię nie zatrzymali za przeproszeniem. Widać że nie masz bladego pojęcia jak działa wszechświat
Tylko że w naturze zwierzęta nie zabijają się dla zabawy.
Rekiny nie lubią tak bardzo ciepłych wód jak i tych zimnych – lubią ciepłe ale bez przesady. Są bardzo sprytne i niektórych kilka gatunków może wpływać do wód słodkich na czas ograniczony
Anonim
Jak przeczytałem, tak się uśmiałem.. 😀
Te strony są bardzo pomocne i można się dużo dowiedzieć;-)
Rekin Wielorybi
Rekin Olbrzymi
Żarłacz Tygrysi
Rekin Pacyficzny
Rekin Polarny
Rekin Kosogonowaty
Rekin Wielkogębowy
Żarłacz ciemoskóry
Rekin kolczasty
Żarłacz białopłetwy
Żarłacz błękitny
Żarłacz biały
Rekin pielęgniarski
Rekin sumiasty
Rekin Whitelya
Rekin ślepy
Żarłacz jedwabisty
Lamna śledziowa
rekin sledziowy
zarłacz sledziowy
Rekin piaskowy wielkooki
rekin młot
Rekin piła
Długoszpar
szescioszpar
siedmioszpar
zarłacz wielkooki
zarłacz ciemoskóry
zarłacz rafowy
zarłacz czarnopłetwy
zarłacz byczy
tawrosz piaskowy
Rekinek islandzki
Rekin szary
Rekin goblin
tawrosz zaglopłetwy
Cretoxyrhina
otodus
megalodon
Helikoprion
parahelikoprion
Rekin wąsaty
Rekin smukły
zarłacz galapagoski
Rekin belizejski
Zarłacz srebrnopłetwy
rekin meksykański
Zarłacz brunatny
zarłacz karaibski
rekin pigmejski
rekin wielkonosy
rekin czarny
rekin jawajski
stetakantus
rekin cytrynowy
rekin kolczasty
rekin falbankowy
rekin lamparci
rekin brązowy
rekin dywanowy
serratolamna
rekin tarkopłetwy
rekinek plamisty
kolczak czarny
lemargo
rekin foremkowy
rekin piaskowy
ostronos pacywiczny
zarłacz ludojad
ostronos długopłetwy
rekin lisi
rekin szary krótkopłetwy
zarłacz milberta
rekinek bacha
rekin marokański
żarłacz miedziany
ptychodus
rekin kopalny
ngangu
rekin ostrozeby
ostronos
rekin widmowiec
squalicorax
rekin łososiowy
spiralozębowiec
rekin gangesowy
rekin łopatogłowy
żarłacz japoński
rekin arktyczny
rekin akwariowy
rekin bambusowy
rekin chochlik
rekin czarnomorski
rekin epoletowy / chyba foremkowy
rekin grenlandzki
zarłacz niebieski / błekitny
rekin rzeczny
rekin rogaty
zarłacz smugowy
rekin tęczowy
rekin tybetanski
zarłacz tępogłowy
zarłacz zolty
negaprion
żarłacz karaibski
zarłacz gruby
więcej nie znam czy znacie jakąś strone gdzie jest wszystki 500 a czy włoczniki się zaliczją do rekinów i kolenie
Kolenie zaliczane są do rekinów, włóczniki nie.
Wykaz rekinów zamieszczamy w oddzielnym komentarzu poniżej. Niemniej ich nazwy są w języku angielskim oraz łacińskim, gdyż nie ma takiego wykazu w języku polskim. Część nazw w języku polskim nie istnieje.
Lista wszystkich gatunków rekinów:
Cow and frilled sharks
• ORDER HEXANCHIFORMES
• Family Chlamydoselachidae (Frilled sharks)
• Genus Chlamydoselachus Garman, 1884
• Chlamydoselachus africana Ebert & L. J. V. Compagno, 2009 (African frilled shark)
• Chlamydoselachus anguineus Garman, 1884 (Frilled shark)
• Family Hexanchidae (Cow sharks)
• Genus Heptranchias Rafinesque, 1810
• Heptranchias perlo (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Sharp-nose sevengill shark)
• Genus Hexanchus Rafinesque, 1810
• Hexanchus griseus (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Blunt-nose sixgill shark)
• Hexanchus nakamurai Teng, 1962 (Bigeyed sixgill shark)
• Hexanchus vitulus Springer and Waller, 1969 (Atlantic sixgill shark)
• Genus Notorynchus Ayres, 1855
• Notorynchus cepedianus (Péron, 1807) (Broad-nose sevengill shark)
Dog and Angelfish sharks
• ORDER SQUALIFORMES
• Family Centrophoridae (Gulper sharks)
• Genus Centrophorus J. P. Müller & Henle, 1837
• Centrophorus atromarginatus Garman, 1913 (Dwarf gulper shark)
• Centrophorus granulosus (Bloch & J. G. Schneider, 1801). (Gulper shark)
• Centrophorus harrissoni McCulloch, 1915 (Dumb gulper shark)
• Centrophorus moluccensis Bleeker, 1860 (Small-fin gulper shark)
• Centrophorus seychellorum Baranes, 2003 (Seychelles gulper shark)
• Centrophorus squamosus (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Leaf-scale gulper shark)
• Centrophorus tessellatus Garman, 1906 (Mosaic gulper shark)
• Centrophorus uyato (Rafinesque, 1810) (Little gulper shark)
• Centrophorus westraliensis W. T. White, Ebert & L. J. V. Compagno, 2008 (Western gulper shark)
• Centrophorus zeehaani W. T. White, Ebert & L. J. V. Compagno, 2008 (Southern dogfish)
• Centrophorus sp. A Not yet described (Mini gulper shark)
• Centrophorus sp. B Not yet described (Slender gulper shark)
• Genus rophorus uyato]] (Rafinesque, 1810) (Little gulper shark)
• Centrophorus westraliensis W. T. White, Ebert & L. J. V. Compagno, Deania D. S. Jordan & Snyder, 1902
• Deania calcea (R. T. Lowe, 1839) (Bird-beak dogfish)
• Deania hystricosa (Garman, 1906) (Rough longnose dogfish)
• Deania profundorum (H. M. Smith & Radcliffe, 1912) (Arrow-head dogfish)
• Deania quadrispinosa (McCulloch, 1915) (Long-snout dogfish)
• Family Dalatiidae (Kitefin sharks)
• Genus Dalatias Rafinesque, 1810
• Dalatias licha (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Kitefin shark)
• Genus Euprotomicroides Hulley & M. J. Penrith, 1966
• Euprotomicroides zantedeschia Hulley & M. J. Penrith, 1966 (Tail-light shark)
• Genus Euprotomicrus T. N. Gill, 1865
• Euprotomicrus bispinatus (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824) (Pygmy shark)
• Genus Heteroscymnoides Fowler, 1934
• Heteroscymnoides marleyi Fowler, 1934 (Long-nose pygmy shark)
• Genus Isistius T. N. Gill, 1865
• Isistius brasiliensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824) (Cookie-cutter shark)
• Isistius plutodus Garrick & S. Springer, 1964 (Large-tooth cookiecutter shark)
• Genus Mollisquama Dolganov, 1984
• Mollisquama parini Dolganov, 1984 (Pocket shark)
• Genus Squaliolus H. M. Smith & Radcliffe, 1912
• Squaliolus aliae Teng, 1959 (Small-eye pygmy shark)
• Squaliolus laticaudus H. M. Smith & Radcliffe, 1912 (Spined pygmy shark)
• Family Echinorhinidae (Bramble sharks)
• Genus Echinorhinus T. N. Gill, 1862
• Echinorhinus brucus (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Bramble shark)
• Echinorhinus cookei Pietschmann, 1928 (Prickly shark)
• Family Etmopteridae (Lantern sharks)
• Genus Aculeola F. de Buen, 1959
• Aculeola nigra F. de Buen, 1959 (Hook-tooth dogfish)
• Genus Centroscyllium J. P. Müller & Henle, 1841
• Centroscyllium excelsum Shirai & Nakaya, 1990 (High-fin dogfish)
• Centroscyllium fabricii (J. C. H. Reinhardt, 1825) (Black dogfish)
• Centroscyllium granulatum Günther, 1887 (Granular dogfish)
• Centroscyllium kamoharai T. Abe, 1966 (Bare-skin dogfish)
• Centroscyllium nigrum Garman, 1899 (Comb-tooth dogfish)
• Centroscyllium ornatum (Alcock, 1889) (Ornate dogfish)
• Centroscyllium ritteri D. S. Jordan & Fowler, 1903 (White-fin dogfish)
• Genus Etmopterus Rafinesque, 1810
• Etmopterus baxteri Garrick, 1957 (New Zealand lanternshark)
• Etmopterus benchleyi V. E. Vásquez, Ebert & Long, 2015 (Ninja lanternshark)
• Etmopterus bigelowi Shirai & Tachikawa, 1993 (Blurred lanternshark)
• Etmopterus brachyurus H. M. Smith & Radcliffe, 1912 (Short-tail lanternshark)
• Etmopterus bullisi Bigelow & Schroeder, 1957 (Lined lanternshark)
• Etmopterus burgessi Schaaf-Da Silva & Ebert, 2006 (Broad-snout lanternshark)
• Etmopterus carteri S. Springer & G. H. Burgess, 1985 (Cylindrical lanternshark)
• Etmopterus caudistigmus Last, G. H. Burgess & Séret, 2002 (Tail-spot lanternshark)
• Etmopterus compagnoi R. Fricke & Koch, 1990 (Brown lanternshark)
• Etmopterus decacuspidatus W. L. Y. Chan, 1966 (Comb-tooth lanternshark)
• Etmopterus dianthus Last, G. H. Burgess & Séret, 2002 (Pink lanternshark)
• Etmopterus dislineatus Last, G. H. Burgess & Séret, 2002 (Lined lanternshark)
• Etmopterus evansi Last, G. H. Burgess & Séret, 2002 (Black-mouth lanternshark)
• Etmopterus fusus Last, G. H. Burgess & Séret, 2002 (Pygmy lanternshark)
• Etmopterus gracilispinis G. Krefft, 1968 (Broad-banded lanternshark)
• Etmopterus granulosus (Günther, 1880) (Southern lanternshark)
• Etmopterus hillianus (Poey, 1861) (Caribbean lanternshark)
• Etmopterus joungi Knuckey, Ebert & G. H. Burgess, 2011 (Short-fin smooth lanternshark)
• Etmopterus litvinovi Parin & Kotlyar, 1990 (Small-eye lanternshark)
• Etmopterus lucifer D. S. Jordan & Snyder, 1902 (Black-belly lanternshark)
• Etmopterus molleri (Whitley, 1939) (Moller’s lanternshark)
• Etmopterus perryi S. Springer & G. H. Burgess, 1985 (Dwarf lanternshark)
• Etmopterus polli Bigelow, Schroeder & S. Springer, 1953 (African lanternshark)
• Etmopterus princeps Collett, 1904 (Great lanternshark)
• Etmopterus pseudosqualiolus Last, G. H. Burgess & Séret, 2002 (False lanternshark)
• Etmopterus pusillus (R. T. Lowe, 1839) (Smooth lanternshark)
• Etmopterus pycnolepis Kotlyar, 1990 (Dense-scale lanternshark)
• Etmopterus robinsi Schofield & G. H. Burgess, 1997 (West Indian lanternshark)
• Etmopterus schultzi Bigelow, Schroeder & S. Springer, 1953 (Fringe-fin lanternshark)
• Etmopterus sculptus Ebert, L. J. V. Compagno & De Vries, 2011 (Sculpted lanternshark)
• Etmopterus sentosus Bass, D’Aubrey & Kistnasamy, 1976 (Thorny lanternshark)
• Etmopterus sheikoi (Dolganov, 1986) (Rasp-tooth dogfish)
• Etmopterus spinax (Linnaeus, 1758) (Velvet-belly lanternshark)
• Etmopterus splendidus Ka. Yano, 1988 (Splendid lanternshark)
• Etmopterus unicolor (Engelhardt, 1912) (Bristled lanternshark)
• Etmopterus viator Straube, 2011 (Traveller lanternshark)
• Etmopterus villosus C. H. Gilbert, 1905 (Hawaiian lanternshark)
• Etmopterus virens Bigelow, Schroeder & S. Springer, 1953 (Green lanternshark)
• Etmopterus sp. Not yet described (Guadalupe lanternshark)
• Etmopterus sp. Not yet described (Chilean lanternshark)
• Etmopterus sp. Not yet described (Papua short-tail lanternshark)
• Genus Trigonognathus Mochizuki & F. Ohe, 1990
• Trigonognathus kabeyai Mochizuki & F. Ohe, 1990 (Viper dogfish)
• Family Oxynotidae (Rough sharks)
• Genus Oxynotus Rafinesque, 1810
• Oxynotus bruniensis (J. D. Ogilby, 1893) (Prickly dogfish)
• Oxynotus caribbaeus Cervigón, 1961 (Caribbean roughshark)
• Oxynotus centrina (Linnaeus, 1758) (Angular roughshark)
• Oxynotus japonicus Ka. Yano & Murofushi, 1985 (Japanese roughshark)
• Oxynotus paradoxus Frade, 1929 (Sail-fin roughshark)
• Family Somniosidae (Sleeper sharks)
• Genus Centroscymnus Barbosa du Bocage & Brito Capello, 1864
• Centroscymnus coelolepis Barbosa du Bocage & Brito Capello, 1864 (Portuguese dogfish)
• Centroscymnus owstonii Garman, 1906 (Rough-skin dogfish)
• Genus Centroselachus Garman, 1913
• Centroselachus crepidater (Barbosa du Bocage & Brito Capello, 1864) (Long-nose velvet dogfish)
• Genus Scymnodalatias Garrick, 1956
• Scymnodalatias albicauda Taniuchi & Garrick, 1986 (White-tail dogfish)
• Scymnodalatias garricki Kukuev & Konovalenko, 1988 (Azores dogfish)
• Scymnodalatias oligodon Kukuev & Konovalenko, 1988 (Sparse-tooth dogfish)
• Scymnodalatias sherwoodi (Archey, 1921) (Sherwood’s dogfish)
• Genus Scymnodon Barbosa du Bocage & Brito Capello, 1864
• Scymnodon ichiharai Ka. Yano & S. Tanaka (II), 1984 (Japanese velvet dogfish)
• Scymnodon macracanthus (Regan, 1906) (Large-spine velvet dogfish)
• Scymnodon plunketi (Waite, 1910) (Plunket’s shark)
• Scymnodon ringens Barbosa du Bocage & Brito Capello, 1864 (Knife-tooth dogfish)
• Genus Somniosus Lesueur, 1818
• Somniosus antarcticus Whitley, 1939 (Southern sleeper shark)
• Somniosus longus (S. Tanaka (I), 1912) (Frog shark)
• Somniosus microcephalus (Bloch & J. G. Schneider, 1801) (Greenland shark)
• Somniosus pacificus Bigelow & Schroeder, 1944 (Pacific sleeper shark)
• Somniosus rostratus (A. Risso, 1827) (Little sleeper shark)
• Somniosus sp. A Not yet described (Longnose sleeper shark)
• Genus Zameus D. S. Jordan & Fowler, 1903
• Zameus squamulosus (Günther, 1877) (Velvet dogfish)
• Family Squalidae (Dogfish sharks)
• Genus Cirrhigaleus S. Tanaka (I), 1912
• Cirrhigaleus asper (Merrett, 1973) (Rough-skin spurdog)
• Cirrhigaleus australis W. T. White, Last & J. D. Stevens, 2007 (Southern mandarin dogfish)
• Cirrhigaleus barbifer S. Tanaka (I), 1912 (Mandarin dogfish)
• Genus Squalus Linnaeus, 1758
• Squalus acanthias Linnaeus, 1758 (Spiny dogfish)
• Squalus acutipinnis Regan, 1908 (Blunt-nose spiny dogfish)
• Squalus albifrons Last, W. T. White & J. D. Stevens, 2007 (Eastern highfin spurdog)
• Squalus altipinnis Last, W. T. White & J. D. Stevens, 2007 (Western highfin spurdog)
• Squalus blainville (A. Risso, 1827) (Long-nose spurdog)
• Squalus brevirostris S. Tanaka (I), 1917 (Japanese shortnose spurdog)
• Squalus bucephalus Last, Séret & Pogonoski, 2007 (Big-head spurdog)
• Squalus chloroculus Last, W. T. White & Motomura, 2007 (Green-eye spurdog)
• Squalus clarkae Pfleger, Grubbs, Cotton & Daly-Engel, 2018, 2018 (Genie’s dogfish)
• Squalus crassispinus Last, Edmunds & Yearsley, 2007 (Fat-spine spurdog)
• Squalus cubensis Howell-Rivero, 1936 (Cuban dogfish)
• Squalus edmundsi W. T. White, Last & J. D. Stevens, 2007 (Edmund’s spurdog)
• Squalus formosus W. T. White & Iglésias, 2011 (Taiwan spurdog)
• Squalus grahami W. T. White, Last & J. D. Stevens, 2007 (Eastern longnose spurdog)
• Squalus griffini Phillipps, 1931 (Northern spiny dogfish)
• Squalus hemipinnis W. T. White, Last & Yearsley, 2007 (Indonesian shortsnout spurdog)
• Squalus japonicus Ishikawa, 1908 (Japanese spurdog)
• Squalus lalannei Baranes, 2003 (Seychelles spurdog)
• Squalus megalops (W. J. Macleay, 1881) (Short-nose spurdog)
• Squalus melanurus Fourmanoir & Rivaton, 1979 (Black-tailed spurdog)
• Squalus mitsukurii D. S. Jordan & Snyder, 1903 (Short-spine spurdog)
• Squalus montalbani Whitley, 1931 (Indonesian greeneye spurdog)
• Squalus nasutus Last, L. J. Marshall & W. T. White, 2007 (Western longnose spurdog)
• Squalus notocaudatus Last, W. T. White & J. D. Stevens, 2007 (Bar-tail spurdog)
• Squalus rancureli Fourmanoir & Rivaton, 1979 (Cyrano spurdog)
• Squalus raoulensis C. A. J. Duffy & Last, 2007 (Kermadec spiny dogfish)
• Squalus suckleyi (Girard, 1854) (Pacific spiny dogfish)
• Squalus sp. Not yet described (Lombok highfin spurdog)
Sawsharks
• ORDER PRISTIOPHORIFORMES
• Family Pristiophoridae (Sawsharks)
• Genus Pliotrema Regan, 1906
• Pliotrema warreni Regan, 1906 (Six-gill sawshark)
• Genus Pristiophorus J. P. Müller & Henle, 1837
• Pristiophorus cirratus (Latham, 1794) (Long-nose sawshark)
• Pristiophorus delicatus Yearsley, Last & W. T. White, 2008 (Tropical sawshark)
• Pristiophorus japonicus Günther, 1870 (Japanese sawshark)
• Pristiophorus lanae Ebert & Wilms, 2013 (Lana’s sawshark)
• Pristiophorus nancyae Ebert & Cailliet, 2011 (African dwarf sawshark)
• Pristiophorus nudipinnis Günther, 1870 (Short-nose sawshark)
• Pristiophorus schroederi S. Springer & Bullis, 1960 (Bahamas sawshark)
Angel sharks
• ORDER SQUATINIFORMES
• Family Squatinidae (Angel sharks)
• Genus Squatina A. M. C. Duméril, 1806
• Squatina aculeata G. Cuvier, 1829 (Saw-back angelshark)
• Squatina africana Regan, 1908 (African angelshark)
• Squatina albipunctata Last & W. T. White, 2008 (Eastern angelshark)
• Squatina argentina (Marini, 1930) (Argentine angelshark)
• Squatina armata (Philippi {Krumweide}, 1887) (Chilean angelshark)
• Squatina australis Regan, 1906 (Australian angelshark)
• Squatina caillieti J. H. Walsh, Ebert & L. J. V. Compagno, 2011 (Philippines angelshark)
• Squatina californica Ayres, 1859 (Pacific angelshark)
• Squatina dumeril Lesueur, 1818 (Atlantic angelshark)
• Squatina formosa S. C. Shen & W. H. Ting, 1972 (Taiwan angelshark)
• Squatina guggenheim Marini, 1936 (Angular angelshark)
• Squatina heteroptera Castro-Aguirre, Espinoza-Pérez & Huidobro-Campos, 2007 (Disparate angelshark)
• Squatina japonica Bleeker, 1858 (Japanese angelshark)
• Squatina legnota Last & W. T. White, 2008 (Indonesian angelshark)
• Squatina mexicana Castro-Aguirre, Espinoza-Pérez & Huidobro-Campos, 2007 (Mexican angelshark)
• Squatina nebulosa Regan, 1906 (Clouded angelshark)
• Squatina occulta Vooren & K. G. da Silva, 1992 (Hidden angelshark)
• Squatina oculata Bonaparte, 1840 (Smooth-back angelshark)
• Squatina pseudocellata Last & W. T. White, 2008 (Western angelshark)
• Squatina squatina (Linnaeus, 1758) (Angelshark)
• Squatina tergocellata McCulloch, 1914 (Ornate angelshark)
• Squatina tergocellatoides J. S. T. F. Chen, 1963 (Ocellated angelshark)
Bullhead sharks
• ORDER HETERODONTIFORMES
• Family Heterodontidae (Bullhead sharks)
• Genus Heterodontus Blainville, 1816
• Heterodontus francisci (Girard, 1855) (Horn shark)
• Heterodontus galeatus (Günther, 1870) (Crested bullhead shark)
• Heterodontus japonicus Maclay & W. J. Macleay, 1884 (Japanese bullhead shark)
• Heterodontus mexicanus L. R. Taylor & Castro-Aguirre, 1972 (Mexican hornshark)
• Heterodontus omanensis Z. H. Baldwin, 2005 (Oman bullhead shark)
• Heterodontus portusjacksoni (F. A. A. Meyer, 1793) (Port Jackson shark)
• Heterodontus quoyi (Fréminville, 1840) (Galapagos bullhead shark)
• Heterodontus ramalheira (J. L. B. Smith, 1949) (White-spotted bullhead shark)
• Heterodontus zebra (J. E. Gray, 1831) (Zebra bullhead shark)
• Heterodontus sp. X Not yet described (Cryptic hornshark)
Mackerel sharks
• ORDER LAMNIFORMES
• Family Alopiidae (Thresher sharks)
• Genus Alopias Rafinesque, 1810
• Alopias pelagicus Nakamura, 1935 (Pelagic thresher shark)
• Alopias superciliosus R. T. Lowe, 1841 (Big-eye thresher shark)
• Alopias vulpinus (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Thresher shark)
• Family Cetorhinidae (Basking sharks)
• Genus Cetorhinus Blainville, 1816
• Cetorhinus maximus (Gunnerus, 1765) (Basking shark)
• Family Lamnidae (Mackerel sharks)
• Genus Carcharodon A. Smith, 1838
• Carcharodon carcharias (Linnaeus, 1758) (Great white shark)
• Genus Isurus Rafinesque, 1810
• Isurus oxyrinchus Rafinesque, 1810 (Short-fin mako)
• Isurus paucus Guitart-Manday, 1966 (Long-fin mako)
• Genus Lamna G. Cuvier, 1816
• Lamna ditropis C. L. Hubbs & Follett, 1947 (Salmon shark)
• Lamna nasus (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Porbeagle shark)
• Family Megachasmidae (Megamouth sharks)
• Genus Megachasma L. R. Taylor, L. J. V. Compagno & Struhsaker, 1983
• Megachasma pelagios L. R. Taylor, L. J. V. Compagno & Struhsaker, 1983 (Megamouth shark)
• Family Mitsukurinidae (Goblin sharks)
• Genus Mitsukurina D. S. Jordan, 1898
• Mitsukurina owstoni D. S. Jordan, 1898 (Goblin shark)
• Family Odontaspididae (Sand tiger sharks)
• Genus Carcharias Rafinesque, 1810
• Carcharias taurus Rafinesque, 1810 (Sand-tiger shark)
• Genus Odontaspis Agassiz, 1838
• Odontaspis ferox (A. Risso, 1810) (Small-tooth sandtiger shark)
• Odontaspis noronhai (Maul, 1955) (Big-eye sandtiger shark)
• Family Pseudocarchariidae (Crocodile sharks)
• Genus Pseudocarcharias Cadenat, 1963
• Pseudocarcharias kamoharai (Matsubara, 1936) (Crocodile shark)
Carpet sharks
• ORDER ORECTOLOBIFORMES
• Family Brachaeluridae (Blind sharks)
• Genus Brachaelurus J. D. Ogilby, 1908
• Brachaelurus colcloughi J. D. Ogilby, 1908 (Blue-grey carpetshark)
• Brachaelurus waddi (Bloch & J. G. Schneider, 1801) (Blind shark)
• Family Ginglymostomatidae (Nurse sharks)
• Genus Ginglymostoma J. P. Müller & Henle, 1837
• Ginglymostoma cirratum (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Nurse shark)
• Ginglymostoma unami Del-Moral-Flores, Ramírez-Antonio, Angulo & Pérez-Ponce de León, 2015 (Pacific nurse shark)
• Genus Nebrius Rüppell, 1837
• Nebrius ferrugineus (Lesson, 1831) (Tawny nurse shark)
• Genus Pseudoginglymostoma Dingerkus, 1986
• Pseudoginglymostoma brevicaudatum (Günther, 1867) (Short-tail nurse shark)
• Family Hemiscylliidae (Bamboo sharks)
• Genus Chiloscyllium J. P. Müller & Henle, 1837
• Chiloscyllium arabicum Gubanov, 1980 (Arabian carpetshark)
• Chiloscyllium burmensis Dingerkus & DeFino, 1983 (Burmese bamboo shark)
• Chiloscyllium griseum J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838 (Grey bamboo shark)
• Chiloscyllium hasselti Bleeker, 1852 (Hasselt’s bamboo shark)
• Chiloscyllium indicum (J. F. Gmelin, 1789) (Slender bamboo shark)
• Chiloscyllium plagiosum (Anonymous, referred to E. T. Bennett, 1830) (White-spotted bamboo shark)
• Chiloscyllium punctatum J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838 (Brown-banded bamboo shark)
• Genus Hemiscyllium J. P. Müller & Henle, 1837
• Hemiscyllium freycineti (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824) (Indonesian speckled carpetshark)
• Hemiscyllium galei G. R. Allen & Erdmann, 2008 (Cenderawasih epaulette shark)
• Hemiscyllium hallstromi Whitley, 1967 (Papuan epaulette shark)
• Hemiscyllium halmahera G. R. Allen, Erdmann & Dudgeon, 2013 (Halmahera epaulette shark)
• Hemiscyllium henryi G. R. Allen & Erdmann, 2008 (Triton epaulette shark)
• Hemiscyllium michaeli G. R. Allen & Dudgeon, 2010 (Leopard epaulette shark)
• Hemiscyllium ocellatum (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Epaulette shark)
• Hemiscyllium strahani Whitley, 1967 (Hooded carpetshark)
• Hemiscyllium trispeculare J. Richardson, 1843 (Speckled carpetshark)
• Hemiscyllium sp. Not yet described (Seychelles carpetshark)
• Family Orectolobidae (Wobbegong sharks)
• Genus Eucrossorhinus Regan, 1908
• Eucrossorhinus dasypogon (Bleeker, 1867) (Tasselled wobbegong)
• Genus Orectolobus Bonaparte, 1834
• Orectolobus floridus Last & Chidlow, 2008 (Floral banded wobbegong)
• Orectolobus halei Whitley, 1940 (Banded wobbegong)
• Orectolobus hutchinsi Last, Chidlow & L. J. V. Compagno, 2006 (Western wobbegong)
• Orectolobus japonicus Regan, 1906 (Japanese wobbegong)
• Orectolobus leptolineatus Last, Pogonoski & W. T. White, 2010 (Indonesian wobbegong)
• Orectolobus maculatus (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Spotted wobbegong)
• Orectolobus ornatus (De Vis, 1883) (Ornate wobbegong)
• Orectolobus parvimaculatus Last & Chidlow, 2008 (Dwarf-spotted wobbegong)
• Orectolobus reticulatus Last, Pogonoski & W. T. White, 2008 (Network wobbegong)
• Orectolobus wardi Whitley, 1939 (Northern wobbegong)
• Genus Sutorectus Whitley, 1939
• Sutorectus tentaculatus (W. K. H. Peters, 1864) (Cobbler wobbegong)
• Family Parascylliidae (Collared carpetsharks)
• Genus Cirrhoscyllium H. M. Smith & Radcliffe, 1913
• Cirrhoscyllium expolitum H. M. Smith & Radcliffe, 1913 (Barbel-throat carpetshark)
• Cirrhoscyllium formosanum Teng, 1959 (Taiwan saddled carpetshark)
• Cirrhoscyllium japonicum Kamohara, 1943 (Saddle carpetshark)
• Genus Parascyllium T. N. Gill, 1862
• Parascyllium collare E. P. Ramsay & J. D. Ogilby, 1888 (Collared carpetshark)
• Parascyllium elongatum Last & J. D. Stevens, 2008 (Elongate carpetshark)
• Parascyllium ferrugineum McCulloch, 1911 (Rusty carpetshark)
• Parascyllium sparsimaculatum T. Goto & Last, 2002 (Ginger carpetshark)
• Parascyllium variolatum (A. H. A. Duméril, 1853) (Necklace carpetshark)
• Family Rhincodontidae (Whale sharks)
• Genus Rhincodon A. Smith, 1828
• Rhincodon typus A. Smith, 1828 (Whale shark)
• Family Stegostomatidae (Zebra sharks)
• Genus Stegostoma J. P. Müller & Henle, 1837
• Stegostoma fasciatum (Hermann, 1783) (Zebra shark)
Ground sharks
• ORDER CARCHARHINIFORMES
• Family Carcharhinidae (Requiem sharks)
• Genus Carcharhinus Blainville, 1816
• Carcharhinus acronotus (Poey, 1860) (Black-nose shark)
• Carcharhinus albimarginatus (Rüppell, 1837) (Silver-tip shark)
• Carcharhinus altimus (S. Springer, 1950) (Big-nose shark)
• Carcharhinus amblyrhynchoides (Whitley, 1934) (Graceful shark)
• Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos (Bleeker, 1856) (Black-tail reef shark)
• Carcharhinus amboinensis (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Pig-eye shark)
• Carcharhinus borneensis (Bleeker, 1858) (Borneo shark)
• Carcharhinus brachyurus (Günther, 1870) (Copper shark)
• Carcharhinus brevipinna (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Spinner shark)
• Carcharhinus cautus (Whitley, 1945) (Nervous shark)
• Carcharhinus cerdale C. H. Gilbert, 1898 (Pacific smalltail shark)
• Carcharhinus coatesi (Whitley, 1939) (Coates’ shark)
• Carcharhinus dussumieri (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (White-cheek shark)
• Carcharhinus falciformis (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Silky shark)
• Carcharhinus fitzroyensis (Whitley, 1943) (Creek whaler)
• Carcharhinus galapagensis (Snodgrass & Heller, 1905) (Galapagos shark)
• Carcharhinus hemiodon (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Pondicherry shark)
• Carcharhinus humani W. T. White & Weigmann, 2014 (Human’s whaler shark)
• Carcharhinus isodon (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Fine-tooth shark)
• Carcharhinus leiodon Garrick, 1985 (Smooth-tooth blacktip shark)
• Carcharhinus leucas (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Bull shark)
• Carcharhinus limbatus (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Black-tip shark)
• Carcharhinus longimanus (Poey, 1861) (Oceanic whitetip shark)
• Carcharhinus macloti (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Hard-nose shark)
• Carcharhinus melanopterus (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824) (Black-tip reef shark)
• Carcharhinus obscurus (Lesueur, 1818) (Dusky shark)
• Carcharhinus perezi (Poey, 1876) (Caribbean reef shark)
• Carcharhinus plumbeus (Nardo, 1827) (Sandbar shark)
• Carcharhinus porosus (Ranzani, 1839) (Small-tail shark)
• Carcharhinus sealei (Pietschmann, 1913) (Black-spot shark)
• Carcharhinus signatus (Poey, 1868) (Night shark)
• Carcharhinus sorrah (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Spot-tail shark)
• Carcharhinus tilstoni (Whitley, 1950) (Australian blacktip shark)
• Carcharhinus tjutjot (Bleeker, 1852) (Indonesian whaler shark)
• Carcharhinus sp. A Not yet described (False smalltail shark)
• Genus Galeocerdo J. P. Müller & Henle, 1837
• Galeocerdo cuvier (Péron & Lesueur, 1822) (Tiger shark)
• Genus Glyphis Agassiz, 1843
• Glyphis gangeticus (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Ganges shark)
• Glyphis garricki L. J. V. Compagno, W. T. White & Last, 2008 (Northern river shark)
• Glyphis glyphis (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Spear-tooth shark)
• Glyphis sp. Not yet described (Mukah river shark)
• Genus Isogomphodon T. N. Gill, 1862
• Isogomphodon oxyrhynchus (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Dagger-nose shark)
• Genus Lamiopsis T. N. Gill, 1862
• Lamiopsis temmincki (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Broad-fin shark)
• Lamiopsis tephrodes (Fowler, 1905) (Borneo broadfin shark)
• Genus Loxodon J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839
• Loxodon macrorhinus J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839 (Slit-eye shark)
• Genus Nasolamia L. J. V. Compagno & Garrick, 1983
• Nasolamia velox (C. H. Gilbert, 1898) (White-nose shark)
• Genus Negaprion Whitley, 1940
• Negaprion acutidens (Rüppell, 1837) (Sickle-fin lemon shark)
• Negaprion brevirostris (Poey, 1868) (Lemon shark)
• Genus Prionace Cantor, 1849
• Prionace glauca (Linnaeus, 1758) (Blue shark)
• Genus Rhizoprionodon Whitley, 1929
• Rhizoprionodon acutus (Rüppell, 1837) (Milk shark)
• Rhizoprionodon lalandii (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Brazilian sharpnose shark)
• Rhizoprionodon longurio (D. S. Jordan & C. H. Gilbert, 1882) (Pacific sharpnose shark)
• Rhizoprionodon oligolinx V. G. Springer, 1964 (Grey sharpnose shark)
• Rhizoprionodon porosus (Poey, 1861) (Caribbean sharpnose shark)
• Rhizoprionodon taylori (J. D. Ogilby, 1915) (Australian sharpnose shark)
• Rhizoprionodon terraenovae (J. Richardson, 1836) (Atlantic sharpnose shark)
• Genus Scoliodon J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838
• Scoliodon laticaudus J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838 (Spade-nose shark)
• Scoliodon macrorhynchos (Bleeker, 1852) (Pacific spadenose shark)
• Genus Triaenodon J. P. Müller & Henle, 1837
• Triaenodon obesus (Rüppell, 1837) (White-tip reef shark)
• Family Hemigaleidae (Weasel sharks)
• Genus Chaenogaleus T. N. Gill, 1862
• Chaenogaleus macrostoma (Bleeker, 1852) (Hook-tooth shark)
• Genus Hemigaleus Bleeker, 1852
• Hemigaleus australiensis W. T. White, Last & L. J. V. Compagno, 2005 (Australian weasel shark)
• Hemigaleus microstoma Bleeker, 1852 (Sickle-fin weasel shark)
• Genus Hemipristis Agassiz, 1843
• Hemipristis elongata (Klunzinger, 1871) (Snaggle-tooth shark)
• Genus Paragaleus Budker, 1935
• Paragaleus leucolomatus L. J. V. Compagno & Smale, 1985 (White-tip weasel shark)
• Paragaleus pectoralis (Garman, 1906) (Atlantic weasel shark)
• Paragaleus randalli L. J. V. Compagno, Krupp & K. E. Carpenter, 1996 (Slender weasel shark)
• Paragaleus tengi (J. S. T. F. Chen, 1963) (Straight-tooth weasel shark)
• Family Leptochariidae (Barbeled houndsharks)
• Genus Leptocharias A. Smith, 1838
• Leptocharias smithii (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Barbeled houndshark)
• Family Proscylliidae (Finback catsharks)
• Genus Ctenacis L. J. V. Compagno, 1973
• Ctenacis fehlmanni (S. Springer, 1968) (Harlequin catshark)
• Genus Eridacnis H. M. Smith, 1913
• Eridacnis barbouri (Bigelow & Schroeder, 1944) (Cuban ribbontail catshark)
• Erida H. M. Smith, 1913 (Pygmy ribbontail catshark)
• Eridacnis sinuans (J. L. B. Smith, 1957) (African ribbontail catshark)
• Eridacnis sp. 1 Not yet described (Philippines ribbontail catshark)
• Genus Proscyllium Hilgendorf, 1904
• Proscyllium habereri Hilgendorf, 1904 (Graceful catshark)
• Proscyllium magnificum Last & Vongpanich, 2004 (Magnificent catshark)
• Family Pseudotriakidae (False catsharks)
• Genus Gollum L. J. V. Compagno, 1973
• Gollum attenuatus (Garrick, 1954) (Slender smooth-hound)
• Gollum suluensis Last & Gaudiano, 2011 (Sulu gollumshark)
• Gollum sp. B Not yet described (White-marked gollumshark)
• Genus Planonasus Weigmann, Stehmann & Thiel, 2013
• Planonasus parini Weigmann, Stehmann & Thiel, 2013 (Dwarf false catshark)
• Genus Pseudotriakis Brito Capello, 1868
• Pseudotriakis microdon Brito Capello, 1868 (False catshark)
• Family Scyliorhinidae (Catsharks)
• Genus Apristurus Garman, 1913
• Apristurus albisoma Nakaya & Séret, 1999 (White-bodied catshark)
• Apristurus ampliceps Sasahara, K. Sato & Nakaya, 2008 (Rough-skin catshark)
• Apristurus aphyodes Nakaya & Stehmann, 1998 (White ghost catshark)
• Apristurus australis K. Sato, Nakaya & Yorozu, 2008 (Pinocchio catshark)
• Apristurus breviventralis Kawauchi, Weigmann & Nakaya, 2014 (Short-belly catshark)
• Apristurus brunneus (C. H. Gilbert, 1892) (Brown catshark)
• Apristurus bucephalus W. T. White, Last & Pogonoski, 2008 (Big-head catshark)
• Apristurus canutus S. Springer & Heemstra, 1979 (Hoary catshark)
• Apristurus exsanguis K. Sato, Nakaya & A. L. Stewart, 1999 (Flaccid catshark)
• Apristurus fedorovi Dolganov, 1985 (Fedorov’s catshark)
• Apristurus garricki K. Sato, A. L. Stewart & Nakaya, 2013 (Garrick’s catshark)
• Apristurus gibbosus Q. W. Meng, Y. T. Chu & S. Li, 1985 (Humpback catshark)
• Apristurus herklotsi (Fowler, 1934) (Long-fin catshark)
• Apristurus indicus (A. B. Brauer, 1906) (Small-belly catshark)
• Apristurus internatus S. M. Deng, G. Q. Xiong & H. X. Zhan, 1988 (Short-nose demon catshark)
• Apristurus investigatoris (Misra, 1962) (Broad-nose catshark)
• Apristurus japonicus Nakaya, 1975 (Japanese catshark)
• Apristurus kampae L. R. Taylor, 1972 (Long-nose catshark)
• Apristurus laurussonii (Sæmundsson, 1922) (Iceland catshark)
• Apristurus longicephalus Nakaya, 1975 (Long-head catshark)
• Apristurus macrorhynchus (S. Tanaka (I), 1909) (Flat-head catshark)
• Apristurus macrostomus Q. W. Meng, Y. T. Chu & S. Li, 1985 (Broad-mouth catshark)
• Apristurus manis (S. Springer, 1979) (Ghost catshark)
• Apristurus melanoasper Iglésias, Nakaya & Stehmann, 2004 (Black roughscale catshark)
• Apristurus microps (Gilchrist, 1922) (Small-eye catshark)
• Apristurus micropterygeus Q. W. Meng, Y. T. Chu & S. Li, 1986 (Small-dorsal catshark)
• Apristurus nakayai Iglésias, 2013 (Milk-eye catshark)
• Apristurus nasutus F. de Buen, 1959 (Large-nose catshark)
• Apristurus parvipinnis S. Springer & Heemstra, 1979 (Small-fin catshark)
• Apristurus pinguis S. M. Deng, G. Q. Xiong & H. X. Zhan, 1983 (Fat catshark)
• Apristurus platyrhynchus (S. Tanaka (I), 1909) (Borneo catshark)
• Apristurus profundorum (Goode & T. H. Bean, 1896) (Deep-water catshark)
• Apristurus riveri Bigelow & Schroeder, 1944 (Broad-gill catshark)
• Apristurus saldanha (Barnard, 1925) (Saldanha catshark)
• Apristurus sibogae (M. C. W. Weber, 1913) (Pale catshark)
• Apristurus sinensis Y. T. Chu & A. S. Hu, 1981 (South China catshark)
• Apristurus spongiceps (C. H. Gilbert, 1905) (Sponge-head catshark)
• Apristurus stenseni (S. Springer, 1979) (Panama ghost catshark)
• Apristurus sp. X Not yet described (Galbraith’s catshark)
• Apristurus sp. 3 Not yet described (Black wonder catshark)
• Genus Asymbolus Whitley, 1939
• Asymbolus analis (J. D. Ogilby, 1885) (Australian spotted catshark)
• Asymbolus funebris L. J. V. Compagno, J. D. Stevens & Last, 1999 (Blotched catshark)
• Asymbolus galacticus Séret & Last, 2008 (Starry catshark)
• Asymbolus occiduus Last, M. F. Gomon & Gledhill, 1999 (Western spotted catshark)
• Asymbolus pallidus Last, M. F. Gomon & Gledhill, 1999 (Pale spotted catshark)
• Asymbolus parvus L. J. V. Compagno, Stevens & Last, 1999 (Dwarf catshark)
• Asymbolus rubiginosus Last, M. F. Gomon & Gledhill, 1999 (Orange spotted catshark)
• Asymbolus submaculatus L. J. V. Compagno, J. D. Stevens & Last, 1999 (Variegated catshark)
• Asymbolus vincenti (Zietz (fi), 1908) (Gulf catshark)
• Genus Atelomycterus Garman, 1913
• Atelomycterus baliensis W. T. White, Last & Dharmadi, 2005 (Bali catshark)
• Atelomycterus erdmanni Fahmi & W. T. White, 2015 (Spotted-belly catshark)
• Atelomycterus fasciatus L. J. V. Compagno & J. D. Stevens, 1993 (Banded sand catshark)
• Atelomycterus macleayi Whitley, 1939 (Australian marbled catshark)
• Atelomycterus marmoratus (Anonymous, referred to E. T. Bennett, 1830) (Coral catshark)
• Atelomycterus marnkalha Jacobsen & M. B. Bennett, 2007 (Eastern banded catshark)
• Genus Aulohalaelurus Fowler, 1934
• Aulohalaelurus kanakorum Séret, 1990 (Kanakorum catshark)
• Aulohalaelurus labiosus (Waite, 1905) (Australian black-spotted catshark)
• Genus Bythaelurus L. J. V. Compagno, 1988
• Bythaelurus alcockii (Garman, 1913) (Arabian catshark)
• Bythaelurus canescens (Günther, 1878) (Dusky catshark)
• Bythaelurus clevai (Séret, 1987) (Broad-head catshark)
• Bythaelurus dawsoni (S. Springer, 1971) (New Zealand catshark)
• Bythaelurus giddingsi J. E. McCosker, Long & C. C. Baldwin, 2012 (Galápagos catshark)
• Bythaelurus hispidus (Alcock, 1891) (Bristly catshark)
• Bythaelurus immaculatus (Y. T. Chu & Q. W. Meng, 1982) (Spot-less catshark)
• Bythaelurus incanus Last & J. D. Stevens, 2008 (Sombre catshark)
• Bythaelurus lutarius (S. Springer & D’Aubrey, 1972) (Mud catshark)
• Bythaelurus naylori Ebert & Clerkin, 2015 (Dusky-snout catshark)
• Bythaelurus tenuicephalus Kaschner, Weigmann & Thiel, 2015 (Narrow-head catshark)
• Genus Cephaloscyllium T. N. Gill, 1862
• Cephaloscyllium albipinnum Last, Motomura & W. T. White, 2008 (White-fin swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium cooki Last, Séret & W. T. White, 2008 (Cook’s swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium fasciatum W. L. Y. Chan, 1966 (Reticulated swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium formosanum Teng, 1962 (Formosa swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium hiscosellum W. T. White & Ebert, 2008 (Australian reticulate swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium isabellum (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Draughtsboard shark)
• Cephaloscyllium laticeps (A. H. A. Duméril, 1853) (Australian swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium pictum Last, Séret & W. T. White, 2008 (Painted swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium sarawakensis Ka. Yano, A. Ahmad & Gambang, 2005 (Sarawak pygmy swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium signourum Last, Séret & W. T. White, 2008 (Flag-tail swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium silasi (Talwar, 1974) (Indian swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium speccum Last, Séret & W. T. White, 2008 (Speckled swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium stevensi E. Clark & J. E. Randall, 2011 (Steven’s swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium sufflans (Regan, 1921) (Balloon shark)
• Cephaloscyllium umbratile D. S. Jordan & Fowler, 1903 (Blotchy swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium variegatum Last & W. T. White, 2008 (Saddled swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium ventriosum (Garman, 1880) (Swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium zebrum Last & W. T. White, 2008 (Narrow-bar swellshark)
• Cephaloscyllium sp. 1 Not yet described (Philippines swellshark)
• Genus Cephalurus Bigelow & Schroeder, 1941
• Cephalurus cephalus (C. H. Gilbert, 1892) (Lollipop catshark)
• Cephalurus sp. A Not yet described (Southern lollipop catshark)
• Genus Figaro Whitley, 1928
• Figaro boardmani (Whitley, 1928) (Australian sawtail catshark)
• Figaro striatus Gledhill, Last & W. T. White, 2008 (Northern sawtail catshark)
• Genus Galeus G. Cuvier, 1816
• Galeus antillensis S. Springer, 1979 (Antilles catshark)
• Galeus arae (Nichols, 1927) (Rough-tail catshark)
• Galeus atlanticus (Vaillant, 1888) (Atlantic sawtail catshark)
• Galeus cadenati S. Springer, 1966 (Long-fin sawtail catshark)
• Galeus eastmani (D. S. Jordan & Snyder, 1904) (Gecko catshark)
• Galeus gracilis L. J. V. Compagno & J. D. Stevens, 1993 (Slender sawtail catshark)
• Galeus longirostris Tachikawa & Taniuchi, 1987 (Long-nose sawtail catshark)
• Galeus melastomus Rafinesque, 1810 (Black-mouth catshark)
• Galeus mincaronei Soto, 2001 (Southern sawtail catshark)
• Galeus murinus (Collett, 1904) (Mouse catshark)
• Galeus nipponensis Nakaya, 1975 (Broad-fin sawtail catshark)
• Galeus piperatus S. Springer & M. H. Wagner, 1966 (Peppered catshark)
• Galeus polli Cadenat, 1959 (African sawtail catshark)
• Galeus priapus Séret & Last, 2008 (Phallic catshark)
• Galeus sauteri (D. S. Jordan & R. E. Richardson, 1909) (Black-tip sawtail catshark)
• Galeus schultzi S. Springer, 1979 (Dwarf sawtail catshark)
• Galeus springeri Konstantinou & Cozzi, 1998 (Springer’s sawtail catshark)
• Genus Halaelurus T. N. Gill, 1862
• Halaelurus boesemani S. Springer & D’Aubrey, 1972 (Speckled catshark)
• Halaelurus buergeri (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838) (Black-spotted catshark)
• Halaelurus lineatus Bass, D’Aubrey & Kistnasamy, 1975 (Lined catshark)
• Halaelurus maculosus W. T. White, Last & J. D. Stevens, 2007 (Indonesian speckled catshark)
• Halaelurus natalensis (Regan, 1904) (Tiger catshark)
• Halaelurus quagga (Alcock, 1899) (Quagga catshark)
• Halaelurus sellus W. T. White, Last & J. D. Stevens, 2007 (Rusty catshark)
• Genus Haploblepharus Garman, 1913
• Haploblepharus edwardsii (Schinz, 1822) (Puffadder shyshark)
• Haploblepharus fuscus J. L. B. Smith, 1950 (Brown shyshark)
• Haploblepharus kistnasamyi Human & L. J. V. Compagno, 2006 (Natal shyshark)
• Haploblepharus pictus (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838) (Dark shyshark)
• Genus Holohalaelurus Fowler, 1934
• Holohalaelurus favus Human, 2006 (Honey-comb catshark)
• Holohalaelurus grennian Human, 2006 (Grinning catshark)
• Holohalaelurus melanostigma (Norman, 1939) (Crying catshark)
• Holohalaelurus punctatus (Gilchrist, 1914) (White-spotted catshark)
• Holohalaelurus regani (Gilchrist, 1922) (Izak catshark)
• Genus Parmaturus Garman, 1906
• Parmaturus albimarginatus Séret & Last, 2007 (White-tip catshark)
• Parmaturus albipenis Séret & Last, 2007 (White-clasper catshark)
• Parmaturus bigus Séret & Last, 2007 (Beige catshark)
• Parmaturus campechiensis S. Springer, 1979 (Campeche catshark)
• Parmaturus lanatus Séret & Last, 2007 (Velvet catshark)
• Parmaturus macmillani Hardy, 1985 (McMillan’s catshark)
• Parmaturus melanobranchius (W. L. Y. Chan, 1966) (Black-gill catshark)
• Parmaturus pilosus Garman, 1906 (Salamander catshark)
• Parmaturus xaniurus (C. H. Gilbert, 1892) (File-tail catshark)
• Parmaturus sp. Not yet described (Rough-back catshark)
• Parmaturus sp. Not yet described (Indonesian filetail catshark)
• Parmaturus sp. Not yet described (Gulf of Mexico filetail catshark)
• Genus Pentanchus H. M. Smith & Radcliffe, 1912
• Pentanchus profundicolus H. M. Smith & Radcliffe, 1912 (One-fin catshark)
• Genus Poroderma A. Smith, 1838
• Poroderma africanum (J. F. Gmelin, 1789) (Striped catshark)
• Poroderma pantherinum (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838) (Leopard catshark)
• Genus Schroederichthys A. Smith, 1838
• Schroederichthys bivius (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838) (Narrow-mouthed catshark)
• Schroederichthys chilensis (Guichenot, 1848) (Red-spotted catshark)
• Schroederichthys maculatus S. Springer, 1966 (Narrow-tail catshark)
• Schroederichthys saurisqualus Soto, 2001 (Lizard catshark)
• Schroederichthys tenuis S. Springer, 1966 (Slender catshark)
• Genus Scyliorhinus Blainville, 1816
• Scyliorhinus boa Goode & T. H. Bean, 1896 (Boa catshark)
• Scyliorhinus cabofriensis K. D. A. Soares, U. L. Gomes & M. R. de Carvalho, 2016
• Scyliorhinus canicula (Linnaeus, 1758) (Lesser-spotted catshark)
• Scyliorhinus capensis (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838) (Yellow-spotted catshark)
• Scyliorhinus cervigoni Maurin & M. Bonnet, 1970 (West African catshark)
• Scyliorhinus comoroensis L. J. V. Compagno, 1988 (Comoro catshark)
• Scyliorhinus garmani (Fowler, 1934) (Brown-spotted catshark)
• Scyliorhinus haeckelii (A. Miranda-Ribeiro, 1907) (Freckled catshark)
• Scyliorhinus hesperius S. Springer, 1966 (White-saddled catshark)
• Scyliorhinus meadi S. Springer, 1966 (Blotched catshark)
• Scyliorhinus retifer (Garman, 1881) (Chain catshark)
• Scyliorhinus stellaris (Linnaeus, 1758) (Nursehound)
• Scyliorhinus tokubee Shirai, S. Hagiwara & Nakaya, 1992 (Izu catshark)
• Scyliorhinus torazame (S. Tanaka (I), 1908) (Cloudy catshark)
• Scyliorhinus torrei Howell-Rivero, 1936 (Dwarf catshark)
• Scyliorhinus ugoi K. D. A. Soares, Gadig & U. L. Gomes, 2015 (Dark freckled catshark)
• Scyliorhinus sp. X Not yet described (Oakley’s catshark)
• Family Sphyrnidae (Hammerhead sharks)
• Genus Eusphyra T. N. Gill, 1862
• Eusphyra blochii (G. Cuvier, 1816) (Wing-head shark)
• Genus Sphyrna Rafinesque, 1810
• Sphyrna corona S. Springer, 1940 (Scalloped bonnethead)
• Sphyrna gilberti Quattro, Driggers, Grady, Ulrich & M. A. Roberts, 2013 (Carolina hammerhead)
• Sphyrna lewini (E. Griffith & C. H. Smith, 1834) (Scalloped hammerhead)
• Sphyrna media S. Springer, 1940 (Scoop-head hammerhead)
• Sphyrna mokarran (Rüppell, 1837) (Great hammerhead)
• Sphyrna tiburo (Linnaeus, 1758) (Bonnethead shark)
• Sphyrna tudes (Valenciennes, 1822) (Small-eye hammerhead)
• Sphyrna zygaena (Linnaeus, 1758) (Smooth hammerhead)
• Family Triakidae (Houndsharks)
• Genus Furgaleus Whitley, 1951
• Furgaleus macki (Whitley, 1943) (Whiskery shark)
• Genus Galeorhinus Blainville, 1816
• Galeorhinus galeus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Tope shark)
• Genus Gogolia L. J. V. Compagno, 1973
• Gogolia filewoodi L. J. V. Compagno, 1973 (Sail-back houndshark)
• Genus Hemitriakis Herre, 1923
• Hemitriakis abdita L. J. V. Compagno & J. D. Stevens, 1993 (Deep-water sicklefin houndshark)
• Hemitriakis complicofasciata T. Takahashi & Nakaya, 2004 (Ocellate topeshark)
• Hemitriakis falcata L. J. V. Compagno & J. D. Stevens, 1993 (Sickle-fin houndshark)
• Hemitriakis indroyonoi W. T. White, L. J. V. Compagno & Dharmadi, 2009 (Indonesian houndshark)
• Hemitriakis japanica (J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839) (Japanese topeshark)
• Hemitriakis leucoperiptera Herre, 1923 (White-fin topeshark)
• Genus Hypogaleus J. L. B. Smith, 1957
• Hypogaleus hyugaensis (Miyosi, 1939) (Black-tip tope)
• Genus Iago L. J. V. Compagno & S. Springer, 1971
• Iago garricki Fourmanoir & Rivaton, 1979 (Long-nose houndshark)
• Iago omanensis (Norman, 1939) (Big-eye houndshark)
• Genus Mustelus H. F. Linck, 1790
• Mustelus albipinnis Castro-Aguirre, Antuna-Mendiola, González-Acosta & De La Cruz-Agüero, 2005 (White-margin fin houndshark)
• Mustelus antarcticus Günther, 1870 (Gummy shark)
• Mustelus asterias Cloquet, 1821 (Starry smooth-hound)
• Mustelus californicus T. N. Gill, 1864 (Grey smooth-hound)
• Mustelus canis (Mitchill, 1815)
• M. c. canis (Mitchill, 1815) (Dusky smooth-hound)
• M. c. insularis Heemstra, 1997 (Caribbean smooth-hound)
• Mustelus dorsalis T. N. Gill, 1864 (Sharp-tooth smooth-hound)
• Mustelus fasciatus (Garman, 1913) (Striped smooth-hound)
• Mustelus griseus Pietschmann, 1908 (Spot-less smooth-hound)
• Mustelus henlei (T. N. Gill, 1863) (Brown smooth-hound)
• Mustelus higmani S. Springer & R. H. Lowe, 1963 (Small-eye smooth-hound)
• Mustelus lenticulatus Phillipps, 1932 (Spotted estuary smooth-hound)
• Mustelus lunulatus D. S. Jordan & C. H. Gilbert, 1882 (Sickle-fin smooth-hound)
• Mustelus manazo Bleeker, 1854 (Star-spotted smooth-hound)
• Mustelus mangalorensis Cubelio, Remya R & Kurup, 2011 (Mangalore houndshark)
• Mustelus mento Cope, 1877 (Speckled smooth-hound)
• Mustelus minicanis Heemstra, 1997 (Dwarf smooth-hound)
• Mustelus mosis Hemprich & Ehrenberg, 1899 (Arabian smooth-hound)
• Mustelus mustelus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Common smooth-hound)
• Mustelus norrisi S. Springer, 1939 (Narrow-fin smooth-hound)
• Mustelus palumbes J. L. B. Smith, 1957 (White-spotted smooth-hound)
• Mustelus punctulatus A. Risso, 1827 (Black-spotted smooth-hound)
• Mustelus ravidus W. T. White & Last, 2006 (Australian grey smooth-hound)
• Mustelus schmitti S. Springer, 1939 (Narrow-nose smooth-hound)
• Mustelus sinusmexicanus Heemstra, 1997 (Gulf smooth-hound)
• Mustelus stevensi W. T. White & Last, 2008 (Western spotted gummy shark)
• Mustelus walkeri W. T. White & Last, 2008 (Eastern spotted gummy shark)
• Mustelus whitneyi Chirichigno F., 1973 (Humpback smooth-hound)
• Mustelus widodoi W. T. White & Last, 2006 (White-fin smooth-hound)
• Mustelus sp. Not yet described (Sarawak smooth-hound)
• Mustelus sp. Not yet described (Kermadec smooth-hound)
• Genus Scylliogaleus Boulenger, 1902
• Scylliogaleus quecketti Boulenger, 1902 (Flap-nose houndshark)
• Genus Triakis J. P. Müller & Henle, 1838
• Triakis acutipinna Kato, 1968 (Sharp-fin houndshark)
• Triakis maculata Kner & Steindachner, 1867 (Spotted houndshark)
• Triakis megalopterus (A. Smith, 1839) (Sharp-tooth houndshark)
• Triakis scyllium J. P. Müller & Henle, 1839 (Banded houndshark)
• Triakis semifasciata Girard, 1855 (Leopard shark)
Alphabetic sort
• A
• African angelshark
• African dwarf sawshark
• African frilled shark
• African lanternshark
• African ribbontail catshark
• African sawtail catshark
• Angelshark
• Angular angelshark
• Angular roughshark
• Antilles catshark
• Arabian carpetshark
• Arabian catshark
• Arabian smooth-hound
• Argentine angelshark
• Arrowhead dogfish
• Atlantic angel shark
• Atlantic sawtail catshark
• Atlantic sixgill shark
• Atlantic sharpnose shark
• Atlantic weasel shark
• Australian angelshark
• Australian blackspotted catshark
• Australian blacktip shark
• Australian grey smooth-hound
• Australian marbled catshark
• Australian reticulate swellshark
• Australian sawtail catshark
• Australian sharpnose shark
• Australian spotted catshark
• Australian swellshark
• Australian weasel shark
• Azores dogfish
• B
• Bahamas sawshark
• Bali catshark
• Balloon shark
• Banded houndshark
• Banded sand catshark
• Banded wobbegong
• Bartail spurdog
• Barbelthroat carpetshark
• Barbeled houndshark
• Bareskin dogfish
• Basking shark
• Beige catshark
• Bigeye houndshark
• Bigeye sand tiger
• Bigeye thresher shark
• Bighead catshark
• Bighead spurdog
• Bignose shark
• Bigeyed sixgill shark
• Birdbeak dogfish
• Blackbelly lanternshark
• Black dogfish
• Blackfin gulper shark
• Blackgill catshark
• Blackmouth catshark
• Blackmouth lanternshark
• Blacknose shark
• Black roughscale catshark
• Blackspot shark
• Blackspotted catshark
• Blackspotted smooth-hound
• Blacktail reef shark
• Blacktailed spurdog
• Blacktip reef shark
• Blacktip sawtail catshark
• Blacktip shark
• Blacktip tope
• Black wonder catshark
• Blind shark
• Blotched catshark, two different species
• Blotchy swellshark
• Blue-eye lanternshark
• Bluegrey carpetshark
• Blue shark
• Bluntnose sixgill shark
• Blunt-nose spiny dogfish
• Blurred lanternshark
• Boa catshark
• Bonnethead shark
• Borneo broadfin shark
• Borneo shark
• Bramble shark
• Brazilian sharpnose shark
• Bristled lanternshark
• Bristly catshark
• Broadbanded lanternshark
• Broadfin sawtail catshark
• Broadfin shark
• Broadgill catshark
• Broadhead catshark
• Broadmouth catshark
• Broadnose catshark
• Broadnose sevengill shark
• Broad-snout lanternshark
• Brownbanded bamboo shark
• Brown catshark
• Brown lanternshark
• Brown shyshark
• Brown smoothhound
• Brownspotted catshark
• Bull shark
• Burmese bamboo shark
• C
• Campeche catshark
• Caribbean lanternshark
• Caribbean reef shark
• Caribbean roughshark
• Caribbean sharpnose shark
• Caribbean smooth-hound
• Carolina hammerhead
• Cenderawasih epaulette shark
• Chain catshark
• Chilean angelshark
• Chilean lanternshark
• Clouded angelshark
• Cloudy catshark
• Coates’ shark
• Cobbler wobbegong
• Collared carpetshark
• Combtooth dogfish
• Combtooth lanternshark
• Common smooth-hound
• Comoro catshark
• Cook’s swellshark
• Cookie-cutter shark
• Copper shark
• Coral catshark
• Creek whaler
• Crested bullhead shark
• Crocodile shark
• Crying catshark
• Cryptic hornshark
• Cuban dogfish
• Cuban ribbontail catshark
• Cylindrical lanternshark
• Cyrano spurdog
• D
• Daggernose shark
• Dark freckled catshark
• Dark shyshark
• Deepwater catshark
• Deepwater sicklefin houndshark
• Dense-scale lantern shark
• Disparate angelshark
• Draughtsboard shark
• Dumb gulper shark
• Dusky catshark
• Dusky shark
• Dusky smooth-hound
• Dusky snout catshark
• Dwarf catshark
• Dwarf catshark
• Dwarf false catshark
• Dwarf gulper shark
• Dwarf lanternshark
• Dwarf sawtail catshark
• Dwarf smooth-hound
• Dwarf spotted wobbegong
• E
• Eastern angelshark
• Eastern banded catshark
• Eastern highfin spurdog
• Eastern longnose spurdog
• Eastern spotted gummy shark
• Edmund’s spurdog
• Elongate carpetshark
• Epaulette shark
• F
• False catshark
• False lanternshark
• False smalltail shark
• Fat catshark
• Fatspine spurdog
• Fedorov’s catshark
• Filetail catshark
• Finetooth shark
• Flaccid catshark
• Flagtail swellshark
• Flapnose houndshark
• Flathead catshark
• Floral banded wobbegong
• Formosa swellshark
• Freckled catshark
• Frilled shark
• Fringefin lanternshark
• Frog shark
• G
• Galapagos bullhead shark
• Galapagos shark
• Galápagos catshark
• Galbraith’s catshark
• Ganges shark
• Garrick’s catshark
• Gecko catshark
• Genie’s dogfish
• Ghost catshark
• Ginger carpetshark
• Goblin shark
• Graceful catshark
• Graceful shark
• Granular dogfish
• Great hammerhead
• Great lanternshark
• Great white shark
• Green-eye spurdog
• Green lanternshark
• Greenland shark
• Grey bamboo shark
• Grey sharpnose shark
• Grey smooth-hound
• Grinning catshark
• Guadalupe lanternshark
• Gulf catshark
• Gulf of Mexico filetail catshark
• Gulf smooth-hound
• Gulper shark
• Gummy shark
• H
• Halmahera epaulette shark
• Hardnose shark
• Harlequin catshark
• Hasselt’s bamboo shark
• Hawaiian lanternshark
• Hidden angelshark
• Highfin dogfish
• Hoary catshark
• Honeycomb Izak
• Hooded carpetshark
• Hooktooth dogfish
• Hooktooth shark
• Horn shark
• Human’s whaler shark
• Humpback catshark
• Humpback smooth-hound
• I
• Iceland catshark
• Indian swellshark
• Indonesian angelshark
• Indonesian filetail catshark
• Indonesian greeneye spurdog
• Indonesian houndshark
• Indonesian shortsnout spurdog
• Indonesian speckled carpetshark
• Indonesian speckled catshark
• Indonesian whaler shark
• Indonesian wobbegong
• Izak catshark
• Izu catshark
• J
• Japanese angelshark
• Japanese bullhead shark
• Japanese catshark
• Japanese roughshark
• Japanese sawshark
• Japanese shortnose spurdog
• Japanese spurdog
• Japanese topeshark
• Japanese velvet dogfish
• Japanese wobbegong
• K
• Kermadec smooth hound
• Kermadec spiny dogfish
• Kitefin shark
• Knifetooth dogfish
• L
• Lana’s sawshark
• Largenose catshark
• Largespine velvet dogfish
• Largetooth cookiecutter shark
• Leafscale gulper shark
• Lemon shark
• Leopard catshark
• Leopard epaulette shark
• Leopard shark
• Lined catshark
• Lined lanternshark
• Lined lanternshark
• Little gulper shark
• Little sleeper shark
• Lizard catshark
• Lollipop catshark
• Lombok highfin spurdog
• Longfin catshark
• Longfin mako
• Longfin sawtail catshark
• Longhead catshark
• Longnose catshark
• Longnose houndshark
• Longnose pygmy shark
• Longnose sawshark
• Longnose sawtail catshark
• Longnose spurdog
• Longnose velvet dogfish
• Longsnout dogfish
• Longnose sleeper shark
• Lowfin gulper shark
• M
• Magnificent catshark
• Mandarin dogfish
• Mangalore houndshark
• McMillan’s catshark
• Megamouth shark
• Mexican angelshark
• Mexican hornshark
• Milk-eye catshark
• Milk shark
• Mini gulper shark
• Moller’s lanternshark
• Mosaic gulper shark
• Mouse catshark
• Mud catshark
• Mukah river shark
• N
• Narrowbar swellshark
• Narrowfin smooth-hound
• Narrowhead catshark
• Narrowmouthed catshark
• Narrownose smooth-hound
• Narrowtail catshark
• Natal shyshark
• Necklace carpetshark
• Nervous shark
• Network wobbegong
• New Caledonia catshark
• New Zealand catshark
• New Zealand lanternshark
• Night shark
• Ninja lanternshark
• Northern river shark
• Northern sawtail catshark
• Northern spiny dogfish
• Northern wobbegong
• Nurse shark
• Nursehound
• O
• Oakley’s catshark
• Oceanic whitetip shark
• Ocellate topeshark
• Ocellated angelshark
• Oman bullhead shark
• Onefin catshark
• Orange spotted catshark
• Ornate angelshark
• Ornate dogfish
• Ornate wobbegong
• P
• Pacific angelshark
• Pacific nurse shark
• Pacific sharpnose shark
• Pacific sleeper shark
• Pacific smalltail shark
• Pacific spadenose shark
• Pacific spiny dogfish
• Painted swellshark
• Pale catshark
• Pale spotted catshark
• Panama ghost catshark
• Papua shorttail lanternshark
• Papuan epaulette shark
• Pelagic thresher shark
• Peppered catshark
• Phallic catshark
• Philippines angelshark
• Philippines ribbontail catshark
• Philippines swellshark
• Pigeye shark
• Pink lanternshark
• Pinocchio catshark
• Plunket’s shark
• Pocket shark
• Pondicherry shark
• Porbeagle shark
• Port Jackson shark
• Portuguese dogfish
• Prickly dogfish
• Prickly shark
• Puffadder shyshark
• Pygmy lanternshark
• Pygmy ribbontail catshark
• Pygmy shark
• Q
• Quagga catshark
• R
• Rasptooth dogfish
• Redspotted catshark
• Reticulated swellshark
• Roughback catshark
• Rough longnose dogfish
• Roughskin catshark
• Roughskin dogfish
• Roughskin spurdog
• Roughtail catshark
• Rusty carpetshark
• Rusty catshark
• S
• Saddle carpetshark
• Saddled swellshark
• Sailback houndshark
• Sailfin roughshark
• Salamander shark
• Saldanha catshark
• Salmon shark
• Sandtiger shark
• Sandbar shark
• Sarawak pygmy swellshark
• Sarawak smooth-hound
• Sawback angelshark
• Scalloped bonnethead
• Scalloped hammerhead
• Scoophead
• Sculpted lanternshark
• Seychelles carpetshark
• Seychelles gulper shark
• Seychelles spurdog
• Sharpfin houndshark
• Sharpnose sevengill shark
• Sharptooth houndshark
• Sharptooth smooth-hound
• Sherwood dogfish
• Shortbelly catshark
• Shortfin mako
• Shortfin smooth lanternshark
• Shortnose demon catshark
• Shortnose sawshark
• Shortnose spurdog
• Shortspine spurdog
• Shorttail lanternshark
• Shorttail nurse shark
• Sicklefin houndshark
• Sicklefin lemon shark
• Sicklefin smooth-hound
• Sicklefin weasel shark
• Silky shark
• Silvertip shark
• Sixgill sawshark
• Slender bamboo shark
• Slender catshark
• Slender gulper shark
• Slender sawtail catshark
• Slender smooth-hound
• Slender weasel shark
• Sliteye shark
• Smallbelly catshark
• Smalldorsal catshark
• Smalleye catshark
• Smalleye hammerhead
• Smalleye lantern shark
• Smalleye pygmy shark
• Smalleye smooth-hound
• Smallfin catshark
• Smallfin gulper shark
• Small-spotted catshark
• Smalltail shark
• Smalltooth sand tiger
• Smoothback angelshark
• Smooth hammerhead
• Smooth lanternshark
• Smoothtooth blacktip shark
• Snaggletooth shark
• Sombre catshark
• South China catshark
• Southern dogfish
• Southern lanternshark
• Southern lollipop catshark
• Southern mandarin dogfish
• Southern sawtail catshark
• Southern sleeper shark
• Spadenose shark
• Sparsetooth dogfish
• Spatulasnout catshark
• Speartooth shark
• Speckled carpetshark
• Speckled catshark
• Speckled smooth-hound
• Speckled swellshark
• Spined pygmy shark
• Spinner shark
• Spiny dogfish
• Splendid lanternshark
• Spongehead catshark
• Spotless catshark
• Spotless smooth-hound
• Spottail shark
• Spotted-belly catshark
• Spotted estuary smooth-hound
• Spotted houndshark
• Spotted wobbegong
• Springer’s sawtail catshark
• Starspotted smooth-hound
• Starry catshark
• Starry smooth-hound
• Steven’s swellshark
• Straight-tooth weasel shark
• Striped catshark
• Striped smooth-hound
• Sulu gollumshark
• Swellshark
• T
• Taillight shark
• Tailspot lanternshark
• Taiwan angelshark
• Taiwan saddled carpetshark
• Taiwan spurdog
• Tasselled wobbegong
• Tawny nurse shark
• Thorny lanternshark
• Thresher shark
• Tiger catshark
• Tiger shark
• Tope shark
• Triton epaulette shark
• Tropical sawshark
• V
• Variegated catshark
• Velvet belly lanternshark
• Velvet catshark
• Velvet dogfish
• Viper dogfish
• W
• West African catshark
• West Indian lanternshark
• Western angelshark
• Western gulper shark
• Western highfin spurdog
• Western longnose spurdog
• Western spotted catshark
• Western spotted gummy shark
• Western wobbegong
• Whale shark
• Whiskery shark
• Whitebodied catshark
• Whitecheek shark
• White-clasper catshark
• Whitefin dogfish
• White-fin smooth-hound
• Whitefin swellshark
• Whitefin topeshark
• White ghost catshark
• White-margin fin smooth-hound
• Whitemarked gollumshark
• Whitenose shark
• Whitesaddled catshark
• Whitespotted bamboo shark
• Whitespotted bullhead shark
• Whitespotted catshark
• Whitespotted smooth-hound
• Whitetail dogfish
• White-tip catshark
• Whitetip reef shark
• Whitetip weasel shark
• Winghead shark
• Y
• Yellowspotted catshark
• Z
• Zebra bullhead shark
• Zebra shark
Wow Bardzo dziękuje